This article goes over the lessons learned and key takeaways from HubSpot's SEO course.
SEO Basics
(Note: Focus is on Google; other search engines are not included in this training)
Why Is SEO Important?
The majority of online experiences involve search:
- 68% of online experiences begin with a search engine
- 53% of all website traffic comes from organic search
- 93% of global traffic comes from Google search, Images, and Maps
SEO / Search Engine Optimization: the practice of increasing the quality and quantity of traffic to a website through organic search results
Performing SEO requires focusing on the end-users and making it easy for search engines to crawl your website
Google prioritizes E-A-T
E-A-T / Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness
- Pages with low E-A-T rank poorly for high-value keywords
SEO is ongoing and cumulative; strategies differ between companies. It's a long-term strategy, and ranking organically can take months.
Benefits of SEO:
- Cost-effective (especially compared to paid advertising)
- Room for your site to grow with a continuous SEO strategy (increase chances of ranking higher)
How Do Search Engines Rank Your Content?
Have a clear understanding of how Google finds, analyzes, and ranks content
How does content rank in search:
- Build discovery (crawling) and relevance (indexing) by creating a lot of high-quality content on topics you want to be known for
- Build authority (ranking) by getting lots of high-quality links to your website
Search Engine ranking stages:
- Discovery / Crawling: Search engine bots discover your content by crawling it (take note of all content in it)
- Relevance / Indexing: Search engine bots decide how relevant your content is by indexing it (based on signals like keywords within the content)
- Authority / Ranking: Search engine bots rank your content in search results based on your site's SEO authority (building credibility through backlinks, for example)
- Authority directly impacts ranking strength
How do you determine authority? (subjective in nature)
- The content is talked about a lot
- The content is referred to often
- The content is cited in other works (backlinks)
Discovery, relevance, and authority are dependent on one another
- If your content isn't relevant, then it has little chance of ranking, no matter how authoritative it is
- If your website isn't authoritative, then it has little chance of ranking, no matter how relevant it is
If websites can't be discovered, they cannot be ranked at all
How to Create an SEO Strategy
Like Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, SEO has its own hierarchy of needs:
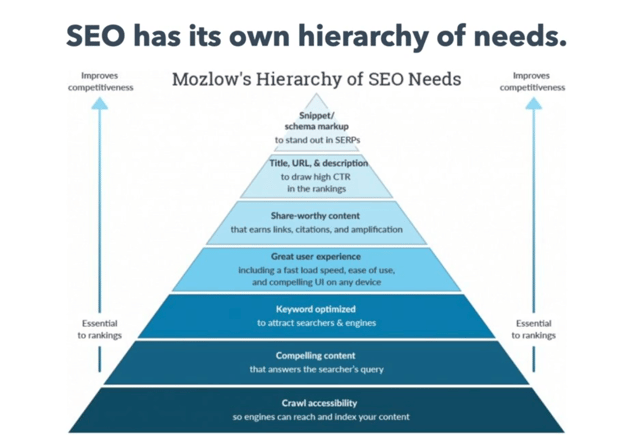
SEO strategies depend on several factors:
- How established is your business online?
- What resources do you need to dedicate to SEO?
- What industry are you in?
If your business is well-known, talked about, and linked to a lot online, your business has good search authority. This means less time building authority through SEO and more time defending your position. Creating more relevant content, which in turn will help you acquire more backlinks, will help defend your position.
If your company is creating a lot of content but not getting many links, then do not only focus on content creation. If your website doesn't have the authority built up yet, then all the content you create isn't going to rank as quickly.
An SEO strategy has website goals and established KPIs (key performance indicators). You must determine your goals for your website and establish those KPIs.
What are the goals for your website:
- Do you want to increase organic traffic?
- Do you want to increase the number of leads from your website?
- Do you want to design a mobile-optimized website?
- Do you want to ensure your website is accessible for those with disabilities?
SMART goals:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Realistic
- Time-bound
KPI / Key Performance Indicator: critical indicators of progress toward an intended result
Core KPIs for SEO include:
- Organic traffic
- Keyword ranking
- Conversion rate
- Bounce rate
- Page load time
- Backlinks built
It's okay to not do something if it's not important for your users. Ultimately, focus on the sers instead of "doing SEO" for the sake of it
How to Measure Your Website's SEO Authority
The most important factor in your website's search authority comes down to link volume and quality of backlinks (Links are a key indicator of a website's SEO authority)
Review your backlink profile to truly measure website authority.
Bakclink Profile: A list of all the sites currently linking to your site (including how they're linking to it and which pages they're linking to)
Backlink profiles measure:
- The number of inbound links to your website
- The number of unique domains that link to your website
- The quality of those links
Cost-effective tools for analyzing backlink profiles:
- Majestic
- ahrefs
- SEM Rush
- MOZ
MOZ has an open site explorer, which scores authority and the number of pages linking to your website.
Measuring website authority and credibility will help you get a better chance of ranking higher.
On-Page and Technical SEO
How to Optimize Content for SEO
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing various front-end and back-end components of your website so that it ranks in search engines and brings in new traffic. On-page SEO changes can be seen by visitors to your website, whereas technical SEO elements are not always visible.
From Google's 'How Search Works' report: "The most basic signal that information is relevant is when a webpage contains the same keywords as your search query. If those keywords appear on the page, or if they appear in the headings or body of the text, the information is more likely to be relevant."
You should be selective with the keywords to use, as it would be helpful for people searching / help their efforts. Focus on just one keyword or key phrase per page.
Core Page Elements:
- Heading tags: an HTML element that provides a hierarchical structure to a web page
- Title tags: an HTML element that specifies a web page's title (displayed on search engine results pages [SERPs])
- External links: links to other websites' content
Heading Tags
Best practices:
- Page should have an H1 tag (ONLY ONE PER PAGE)
- Subsequent headings on the page should have an H2, H3, etc.
- Use your primary keyword in your page title
Title Tags
Designed for people who are NOT on your site, displayed on SERPs (search engine results pages)
Title tags can generally match the page heading
- If the page heading is long, the title should be shorter so it fully shows on Google
Best practices:
- Include your primary keyword in the title tag
- Keep your title under 60 characters if possible
- Make sure both your page heading and title answer the searcher's primary question
External Tags
Linking to quality external content shows that you've done research.
Use optimizations in HubSpot within the page and blog editor
Allowing Google to Index Your Pages
Three primary functions of Search Engines:
- Crawl: Search web pages and look over the code and content for each URL
- Index: Store and organize the information it finds from crawling
- Rank: Provide the pieces of content that best match a person's search query
Google crawling bots look for new sites, updates to existing pages, and broken links
site: <Your site domain> in Google search will determine how many pages are indexed in Google.
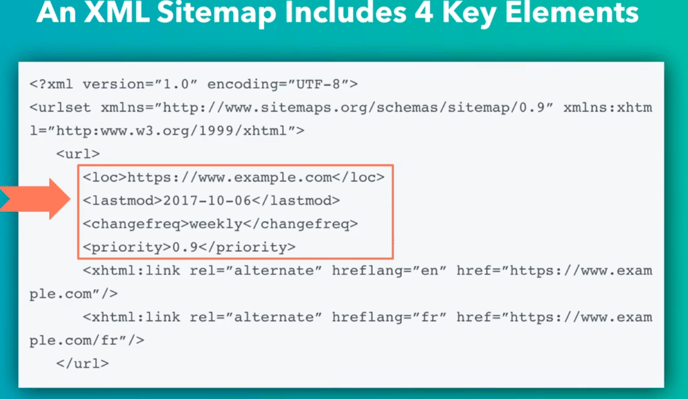
Sitemap: a file of code that lives on your web server and lists all of the relevant URLs your website is carrying
An XML sitemap is a crucial component of a blog, where article pages are constantly bumped further back into the website's archive as new content is published.
XML sitemap contains 4 key elements:
- URL location (full URL to the page)
- Last modified date
- Change frequency (Never, Yearly, Monthly, Weekly, Daily, Hourly, or Always)
- Page priority number (indicates relative priority of pages)
Roles involved in structuring a sitemap:
- Marketing: defines the structure of the site
- Development: build an XML sitemap file based on the structure
- IT: sitempa lives on the server, IT will get it there
- Legal: make sure the site does not have any outstanding copyright issues
The further away a page is from the original homepage URL of your site, the worse it is for that page's SEO.
Best Practices: Take inspiration from companies similar to you (varies based on industry)
You'll need to update the sitemap yourself and resubmit it any time you make significant changes to your website. Otherwise, you'll have to wait for search engines to identify, crawl, and index
your new pages themselves. (HubSpot will update your sitemap file automatically as new pages are generated)
XML Sitemaps tools: Screaming Frog & XML-Sitemaps.com
How to submit a sitemap directly to a search engine from a sitemap generator:
- Sign in to Google Search Console (GSC)
- Add the domain name
- Click "Go to Property"
- Click sitemaps and submit the sitemap link (EX: www.yourcompany.com/sitemap.xml)
- Submit sitemap
Writing and Editing Meta Descriptions
Meta Description: an HTML attribute that provides a brief summary of a webpage
Meta descriptions are not an official ranking factor for Google search results, but they help viewers understand the webpage content
3 Reasons why you need a Meta Description:
- Increases clickthrough rates and visits from organic search
- gives the right people the right information
- increases visits from social media
Advanced search: allows people to specify or exclude terms in the search results
How to conduct an advanced search:
- Explicit Phrase: you use quotes around the word that you want to appear
- Exclude Words: add a minus sign before the word that you want to exclude
- This OR That: add OR in all caps to view results for multiple search terms
Social networks also display meta descriptions when content is published.
Best practices for writing a meta description:
- Write compelling content (Meta description conveys the value of your page to the viewers)
- Include one or two keywords (Focus on one or two unique keywords in the meta description)
- Aim for 155-160 characters (pixel-based limit in SERP, character limit avoids the possibility of it being cut off)
- Avoid non-alphanumeric characters
Writing Descriptive Link Text
Link description: clickable word(s) in a hyperlink
Link description best practices:
- Stay on topic, don't use text that has no relation to the page's content
- Don't use the page's URL as the link description, unless you have a good reason to do so, such as referencing a site's new address
- Keep descriptions concise, aim for a few words or a short phrase
- Format links so that they're easy to spot
Internal Linking
Internal Link: a link from one page of a website to another on your website
Internal linking passes authority / link juice, though not as important as backlinks
The right internal links help Google learn the following about your page:
- Relevance
- Relationship to your other pages
- Value
Use topic clusters to arrange your website architecture by grouping content around specific topics related to your business.
Make sure all internal links are "follow" links, not "nofollow"
URL Structure
URL / Uniform Resource Locator: specifies the location of a resource on the web
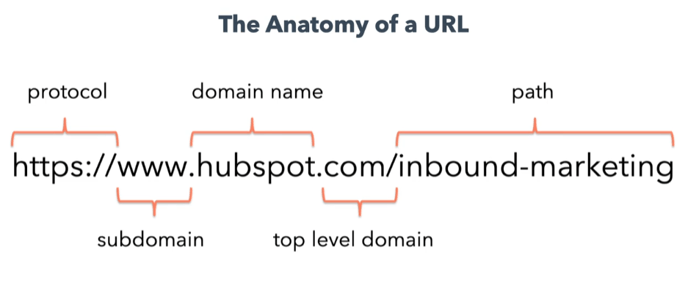
URLs affect SEO in a few ways:
- Improve user experience
- They're a ranking factor in search engines
- They help users and search engines understand what your content is about
Best Practices:
- Use hyphens between words
- Keep them short and simple
- Describe the page contents
- Make sure they're descriptive
- Include your target keyword in your URL
Technical SEO Basics
Technical SEO: The practice of improving technical aspects of a website to help search engines crawl and index it more effectively
Basic technical SEO elements:
- Robots.txt: a text file that instructs search engine bots on how to crawl a website's pages
- Canonicalization: an HTML element that search engines use to manage duplicate content
- Protocols: indicate how a browser should retrieve information about the web page
- Redirect codes: A way to send users and search engines to a different URL from the one originally requested
- Site speed
Robots.txt
Use for pages you DO NOT want search engines to crawl and add to their index.
Common uses for Robots.txt include:
- Customer profiles
- Staging sites
- Internal search results
- Certain files, like images or PDFs
- Duplicate content
Basic format for Robots.txt:
- User-agent: [user-agent name]
- Disallow: [URL string not to be crawled]
Canonical Tag
Canonization can apply to pages with duplicate content or similar URLs (EX: example.com VS www.example.com)
Best practices:
- Use-self self-referential canonical tags
- Canonicalize your website's homepage
- Audit your canonical tags
Protocols
HTTP and HTTPS are standard. All websites should use HTTPS to avoid insecure warnings.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) / TLS (Transport Layer Security): what allows you to create that secure, encrypted experience on your site
Make sure your website has a valid SSL certificate (HubSpot provides automatically)
Redirect Codes
Most common redirect codes:
- 301, or "Moved Permanently" -> send users to a new page that replaced the old one
- 302, or "Moved Temporarily" -> send users elsewhere while a page is under construction
Site Speed
Optimizing images helps speed up a website. The bigger the file size, the longer it takes to load. Upload images at the exact dimensions you plan on displaying them. Strike a balance between the lowest possible quality and file size.
Mobile optimization is critical, as over 50% of internet activity is on mobile. Use Google's mobile-friendly test to check your website's accessibility.
Responsive Design: the method of designing webpages that appear optimally on all devices (takes into account all screen sizes)
Be aware of Pop-Ups on mobile, as they may interfere with a user's ability to navigate the page; this will negatively impact the user experience and your SEO.
Resizing and Compressing Images
Resizing and compressing can help with load times.
- Resize Image: Images must be the size that will be displayed on the page (Use Photoshop or Squoosh)
- Compress Image: reduces file size, reducing load times (Use Tiny PNG to compress images in bulk)
Images should aim to be less than 100 KB.
Keyword Research for SEO
Why Keyword Research is Important
Keywords: the words and phrases that people type into search engines
Keyword Research: the process of finding and analyzing search terms that people enter into search engines with the goal of using that data for a specific purpose
Keyword research helps answer questions like:
- What are people searching for?
- How many people are searching for it?
- What format do they want to receive information in?
- How difficult will it be to rank for that search query?
Types of search terms:
Head Terms: single-word keywords with lots of search volume and competition (EX:
marketing, insurance)
Search Volume: the number of times a particular keyword is entered into a search engine per month
Body Keywords: 2-3 word phrases with decent search volume, but slightly more specific
than head terms and with slightly less competition (EX: marketing automation, car insurance)
Long Tail Keywords: more specific phrases that don't get as much search volume but tend to be less competitive (the majority of searches online [DOES NOT refer to length of query])
Examples of long tail keywords:
- "How to apply sunscreen"
- "How often should you apply sunscreen"
- "When to apply sunscreen"
Keyword strategies should contain a mix of long tail and body keywords guided by head terms
Why Are Topic Clusters Important
Adding more content to an outdated existing site architecture can make it harder for
Google to find and rank your content.
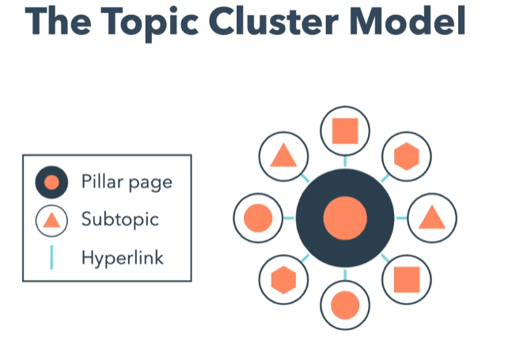
Content must have a positive user experience for both the viewer and the search engine. Creating targeted clusters of relevant content covering specific topics in depth is how to approach this. Pillar pages are needed to organize this.
Pillar Page: is a website page that covers a specific topic in depth and is linked to a cluster of related content
How to do Keyword Research
There is NO correct way to do keyword research.
Steps to Keyword Research:
- Understand your customers and their goals
- Decide which topics you want to be known for
- Find out what terms people are searching for online
- Note search volume and competition
- Organize your keywords into topic clusters
- Prioritize which topic cluster you're going to focus on first
Step 1: Understand your customers and their goals
Create buyer personas with SEO in mind
Buyer Persona: a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on real data and some educated speculation about demographics, behaviors, motivations, and goals
Step 2: Decide which topics you want to be known for
What topics are people searching for that are related to your business?
Start by making a list of all the important, relevant topics for your business. It's best to prioritize which topics to focus on
Step 3: Find out what terms people are searching for online
Start at the topic level, then zoom in. Topics can act as root words when doing research.
Tools for keyword research:
- Google Keyword Planner
- Moz Keyword Explorer
- Answer the Public
- Keyword Surfer Google Extension
- KeywordsEverywhere Google Extension
Step 4: Note search volume and competition
Take note of the monthly search volume and competition for each keyword you're interested in targeting.
Not worth going for keywords with zero search volume. If you're going for keywords where big, authoritative companies are dominating the search results before, avoid those as well.
Check to see what existing content is being ranked and see how you can offer unique value.
Check for trending keywords (use Google Trends). Perform competitive analysis for keywords (can use an incognito browser window to check who is ranking well for specific queries)
Step 5: Organize your keywords into topic clusters
Map out and organize keywords into related clusters around a given topic.
Step 6: Prioritize which topic cluster you're going to focus on first
Depends on your goals and the search intent of your chosen keywords.
Buyer's Journey: the active research process someone goes through leading up to a purchase
3 Stages of the Buyer's Journey:
- Awarenesss
- Consideration
- Decision
Link Building for SEO: Scaling Your Backlink Strategy
Why Is Link Building Important for SEO
Google measures how interesting other people think your content is. This is measured primarily through backlinks.
Backlinks: a signal to Google that your site is a high-quality resource people want to reference
More backlinks + higher quality backlinks = higher ranking results
Link Building: the process of manually encouraging people to link to your website from theirs
The key to effective link building is to complement creating great content with manually building
links.
NOTE: Not all content is naturally linkable (EX: Product pages typically don't receive organic links)
How Many Links Does Your Content Need to Rank on Page One
To rank highly, you need as many links as other ranked results on page 1.
How to calculate a baseline target for how many links you'll need:
- Choose a broad topic that you want to be known for
- Plug that topic into Google and run a search
- Run the URLs for the top 10 results through a link-checking tool
- Calculate the average number of root domains linking to these sites
Do not try to stand out and be different; try to follow those who are ranking well.
Why Relationships Are the Key to Link Building at Scale
Relationships are generally the best way to build links. Carefully and tactfully connect with those who want to link to your website.
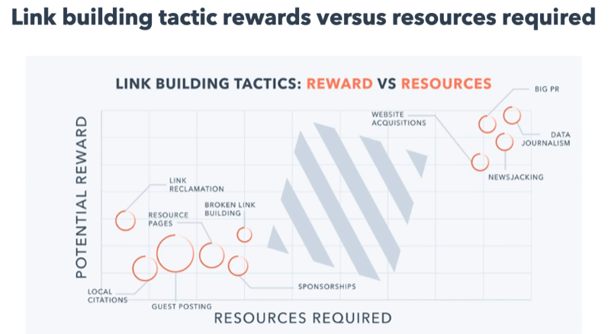
The only way to scale low-risk, low-reward link-building tactics is by building lasting relationships. Freelance journalists are great resources for link building.
Relationship-building should always start with you delivering value.
Consider how your business is currently doing relationship-building:
- What relationships does your organization already have with journalists, bloggers, influencers, and others who might link to your site?
- Whom do you wish your organization had a relationship with?
- What value can you offer them to initiate a relationship?
How to Scale Link Building Using Press Request Alerts
Big publications and influencers can offer high-quality links.
Press Request Alerts: requests that journalists send out asking for sources of information (like quotes on a certain topic from an industry)
Read requests that are relevant and respond quickly, and then you can get a link from a high-quality publication.
List of services for press request alerts:
- Free Services
- HARO
- Source Bottle
- NARO PR
- #JournoRequest / #PRrequest (Twitter hashtags used by journalists)
- Paid services
- Muck Rack
- Gorkana
You'll get hundreds of requests, but you must respond quickly. As a tip, use your email client's filters to surface the requests that have specific keywords and phrases that are relevant to you.
How to effectively respond to press request alerts:
- Sign-up for one PRA service to start
- Browse these requests without responding for 1-2 weeks
- Make a list of thought leaders in your organization who might offer quotes on relevant topics
- Email them asking for quotes across those topics

Optimizing Your Website for Rich Results
What Are Rich Results
Rich results = SERPs
SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages): Google's response to a user's search query
SERPs can include:
- Organic results
- Paid ads
- Featured snippets
- Knowledge graphs
- Rich results
SERPs determine how your site appears on Google, primarily the first page. Most SERPs include some type of rich results.
Rich Results: visually enhanced search results that provide supplemental information to the title, URL, and meta description of a web page
Rich results only appear for pages with a certain type of information.
Common rich results to optimize for:
- Image packs
- Local packs
- Reviews
- Recipes
- Site links
Image Packs
Results are displayed as a horizontal row of images that click through to a Google Images search.
Image optimization best practices:
- Include a descriptive file name for your image and detailed alt text
- Make sure your image URL is readable
- Optimize your image's size
- Include a title attribute
Local Packs
Contains 3 physical that Google deems most relevant to the search query.
Best for local / brick-and-mortar businesses. Make sure the Google My Business profile is up to date for it to show accurately on a local pack.
Reviews
Review stars and ratings data can be displayed for products, recipes, and other relevant items. Reviews and ratings data will have a higher click-through rate.
Recipes
For recipe searches, a carousel of recipes is displayed, including rating information and ingredients.
Site Links
When someone searches for an exact domain, Google can display an expanded list of up to 10 site links. Works best for large, known branded sites.
What is Structured Data
Structured data helps Google to better understand the contents of your pages and what your website is all about, so it can provide more relevant, helpful results to searchers.
Structured Data: A standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content (structured data is a markup language)
Structured data makes it easier for Google to understand what images and content are about, so it can accurately display that content in search results. These can be displayed as "rich results" or "rich snippets".
There are no guarantees that Google will create a rich snippet of your page, even with added structured data. Structured data only makes your page eligible for rich results.
Schema.org: the organization that creates the standardized language and rules used for structured data (accepted and understood by Google)
JSON-LD is the recommended format.
JSON-LD: a script that can be placed within a web page to communicate structured data to search engines
3 ways to implement structured data:
- Work with a developer
- Use a plugin
- Add it manually
Steps to add structured data to a page:
- In the head HTML of your web page, add a script element set to JSON-LD
- Inside the script element, tell Google you're using Schema.org structured data
- Based on the type of content you're describing, tell Google which kind of structured data you're using
- Add all the required and recommended properties to give Google more information about the content being described
Make sure to test your structured data by using Google's Rich Results Test and Structured Data Testing Tool.
Optimizing Featured Snippets
Featured Snippet: A featured snippet is a summary of an answer to a user's query, which is displayed on top of Google search results; It's extracted from a webpage and includes the page's title and URL.
Content that isn't necessarily #1 can appear in a featured snippet ABOVE #1.
3 Reasons to care about featured snippets:
- Featured snippets show up for a lot of the terms your target customers are searching for
- Featured snippets often show up first for voice search results (growth in voice search results)
- If you don't have an effective strategy for capturing how customers are changing the way they search, you will fail to attract them
Capturing a featured snippet by optimizing blog posts that already rank in the top five positions in search results.
How to optimize for the featured snippet:
- Use Search Console to see if your post ranks 1 - 5 for any significant keywords
- See if the featured snippet appears in the search for those keywords
- Optimize your posts for the featured snippet (Format is critical for optimization)
- Submit URLs to Google to be recrawled
- Measure snippet results for
How to Report on SEO
How to Report on Your SEO Efforts
SEO is an iterative process. You can't go after everything all at once. You have to make a change and then wait to see if it made a difference. Reporting helps you figure out what's working and what isn't, and pivot your strategy accordingly.
DO NOT over-optimize content, as it could affect your rank. You cannot collect quality data if too many changes are made quickly.
How to monitor results:
- Use GSC to check your search performance and rank for a keyword or page
- Use Google Analytics to track organic traffic to a page
